Data is everywhere. Today, data is increasingly large and strongly distributed, requiring a different way of storing it than traditional. It is other storage that will create breakthroughs in accessing insights from data. In this article, we cover distributed storage and data fusion, which are the most advanced ways of storing data we have.
1. What is distributed storage?
1.1. Overview of distributed storage
Distributed storage or distributed data storage is a way to call a system that stores data on many different machines. That could be physical servers or data centers. This system is usually designed with distributed clusters that share the same synchronization mechanism and are centrally managed. You can build a distributed storage or use services from vendors.
1.2. How does distributed storage work?
Behind a distributed storage system is a system of complex jobs. To work, the system performs three main jobs including data partitioning, query routing, and replication. These jobs are performed in the same order as listed below. Let’s talk about data partitioning first.
To store data in a distributed manner, we need to partition the data. There are many different types of data, so there will be many ways of partitioning. The two main and used partitioning methods are vertical partitionings and horizontal partitioning.
- With vertical partitioning, the data is divided by the data field. Often these fields are related or have the same query frequency, etc.
- With horizontal partitioning, data is divided horizontally. This method is often used for data that is schema-like, or difficult to process without separation. Horizontal partitioning can be supported by algorithms and dynamic division, to optimize storage efficiency.
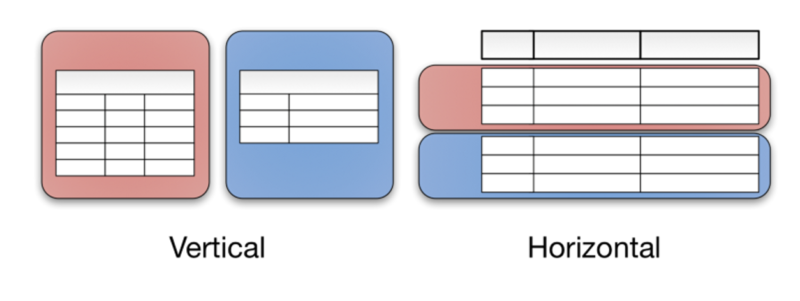
Vertical partitioning and Horizontal partitioning. Source: towards data science (https://towardsdatascience.com/database-terminologies-partitioning-f91683901716)
B. Query Routing
Query routing is the next step. This is to route the correct machine from the client-side to the correct back-end. Distributed data storage systems are often built to serve multiple clients at the same time. Proper routing is essential and is done at many different levels. Three of them can be client-side, proxy-based, or server-side.
C.Replication
Distributed data has the potential to be lost when operating in problematic clusters. If not replicated, data loss can affect data queries as well as disrupt system operation. In addition, copying increases read speed and reduces data latency.
As mentioned above, distributed storage systems work in many ways, and understanding the above concepts is important to design a system that is right for your data and purposes.
1.3. Benefits of distributed storage
The above can also partially explain the benefits of distributed storage. These are the benefits that distributed storage offers:
- Scalability: It is relatively easy to scale the system by simply adding nodes to compute clusters. Thanks to this ability, the system is suitable for the majority of people today, when the data increases very quickly.
- Redundancy: Thanks to the ability to replicate data, the system is able to protect data well, even in the event of a failure or natural disaster at the storage site.
- Cheaper cost: Compared to building a traditional storage system yourself. hosting on the distributed system of providers saves you money on investment and reduces operational risk.
- Faster and more powerful: The performance of distributed storage is further appreciated by the massive computing power of the servers and the ability to access a lot of data from many customers quickly.
1.4. Distributed storage products in real life
Multiple providers for distributed data storage. We list three of them:
- Cloud Spanner is Google’s comprehensive database management service. This service is universally serviceable, has an automatic operation, good security, and high availability
- Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) is a scalable, highly secure object-based data storage service that serves a wide range of business, technology, cloud, IoT data storage.
- Azure Storage is Microsoft’s cloud storage solution with high scalability, good security, ease of access, and availability.
2. What is data fusion?
2.1. Overview of data fusion
We already know how to store huge data. It is to scatter them. Great! But getting information from diverse data from many different sources is another story. Data fusion is a way to get information from different sources for better quality information. For example, to get soil information, information from multiple sensors is better than one. And information from many types of sensors such as water, temperature, light will bring even more valuable information. In business operations, information from many different sources, if well aggregated, will create a lot of value. When it comes to data fusion, the JDL data fusion framework is often mentioned. You can see them below
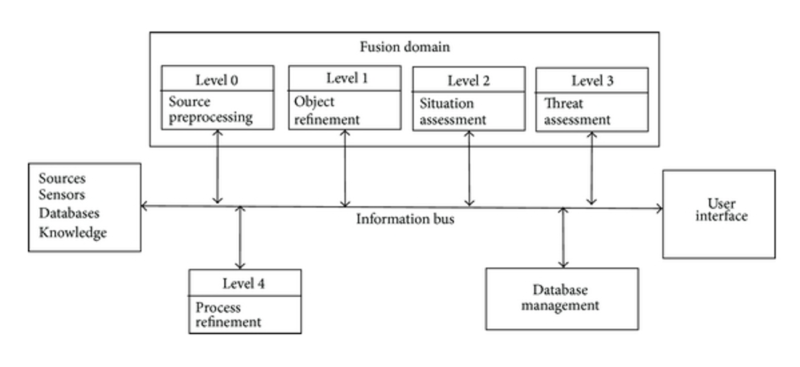 JDL data fusion framework. Source: researchgate (https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-JDL-data-fusion-framework_fig4_259003916)
JDL data fusion framework. Source: researchgate (https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-JDL-data-fusion-framework_fig4_259003916)
2.2. Benefits of data fusion
We want to emphasize that there are many approaches to data fusion. We will discuss this in more detail later. Before getting to the actual example, let’s summarize the benefits of data fusion:
- More valuable information: More data sources can be accessed, aggregated information will bring greater value, more savings.
- More ways to exploit information: Data is more and more diverse, building data fusion architectures for many fields help us make full use of data.
- Apply more domains: Different sectors of a large context will benefit if the information is used not only for the field it spawns but also for other areas, as this will generate many insights.
2.3. Data fusion architectures in real life
Scientists in the UK and China have built various data fusion architectures. The algorithms behind these architectures are those that use machine learning and algorithms for data mining, storage, and analysis. Data fusion often plays an important role in large projects.
- Wearable health monitoring: Scientists from the UK have applied data fusion technology in analyzing data from wearable health monitoring. The data in the sensor of the wearable sensor can be motion, biometric, or from the environment. From these data, the scientists built the following architecture.
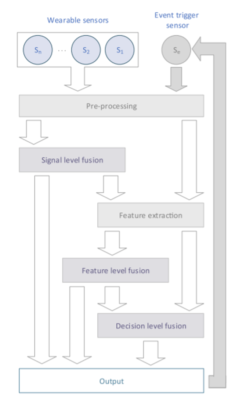
Data fusion architecture for wearable health monitoring systems. Source: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/222826507.pdf
The results obtained from the trials offer the potential for the commercialization of a smart wearable device capable of detailed user health monitoring.
- Smart City: Chinese scientists have proposed and evaluated a smart city model using data fusion. They argue that the technology responds to the growing demand for data, and the resulting data fusion unlocks high-value insights, which in turn leads to a truly smart city built from data.
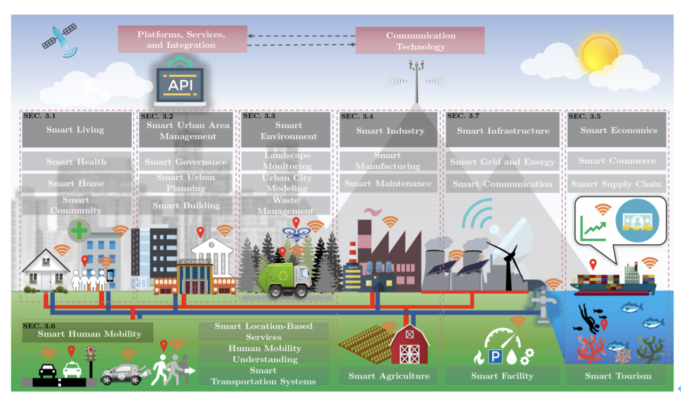 Areas in smart cities can use data fusion. Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.11933.pdf
Areas in smart cities can use data fusion. Source: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.11933.pdf
3. Conclusion
Faced with huge amounts of data, we can ignore them, as we have always done, or take advantage of the huge data source out there to create new achievements. Distributed storage or data fusion are great ways to leverage data, bringing new opportunities to the big data, cloud, IoT industries. Capturing data, more than ever, is key to the growth of every business. We understand this deeply and are always ready to embrace the data with you.
