
Source: https://bff-tech.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/iot–600×424.jpg
The need for communication is human nature to collaborate and exchange our thoughts. The same thing applies to machines and manufacturers. Machines need to stay connected which provides better automation and synchronization. Moreover, people demand real-time data about the inventory, status of their machines to optimize the production process.
In this article, we will illustrate the concept of “machine to machine”(M2M) – an enabling technology in the Internet of things. In addition, we also discuss how “device to device” communication (D2D) differ from other traditional cellular connections.
1. An overview of IoT

Source: https://bff-tech.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/iot–600×424.jpg
Internet of things is a system that contains physical devices. Those devices usually come with sensors, computer chips, etc, and network connectivity. IP addresses are assigned to them so that they can transfer the data they collected to other devices over the Internet without requiring human interaction.
‘Things’ in IoT can be sensed or remotely controlled over the existing network infrastructure, and increase digital transformation level. As a result, companies can not only gain more efficiency, reliability, and benefits but also can reduce the labor required and focus on the decision-making process based on the data that come from ‘things’.
The widespread use of the Internet makes IoT becomes even more powerful. IoT now can be integrated into a wide variety of different devices, services, systems, and enable spanning horizontally across domains. IoT is expected to bring more efficiency than that of machine-to-machine transmission.
2. What is Machine-to-machine (M2M)
Together with IoTs, Machine-to-machine communication provides the connectivity and automation ability to improve many aspects of life from the economy to our daily activities.
Initially, so that people can focus on other important tasks. However, recently the term ‘M2M’ is generally about the technologies such as wired or wireless connections that are used to connect machines, devices without human intervention. M2M enables a large amount of data to be connected and transfer data efficiently. Therefore, they can reduce the cost, the efficiency of the production and be used to transfer private information in a company.
3. Differences between IoT and M2M
Source: https://www.ethings.vn/su-khac-nhau-giua-cong-nghe-m2m-va-iot/
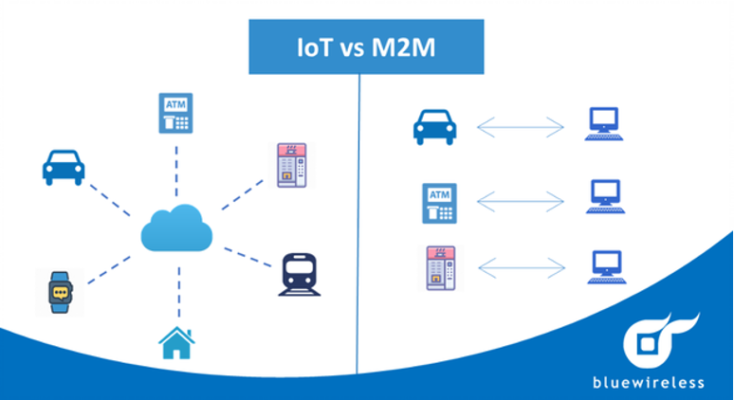
IoT and M2M seem to have a lot in common, they both refer to the interconnection and sharing data between devices with embedded chips, sensors. Therefore not surprisingly, we may easily consider them as one.
However, there is a distinction between them. IoT is a broader system of devices where every device has an IP address and can communicate over the internet platform whereas M2M concentrates on the direct flow of information between two devices and supports a point-to-point connection.
An example of M2M could be a revolutions per minute (RPM) sensor on a mill sending data directly to only one smartphone.
M2M also ships with some security features because of its characteristics:
- End-to-end encryption because the communication is established between 2 devices.
- When hackers attack, only information between some pairs of devices can be jeopardized.
4. Device-to-Device (D2D) communication
Source: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Device-to-device-communication-in-5G-cellular-and-Tehrani-Uysal/7f5326ad8685a006ee19f37230d9f4cf0eacf89e/figure/3
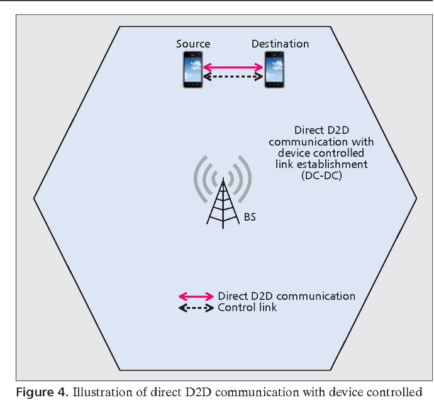
The cellular network is one of the most blooming technologies recently with its fifth-generation (5G) which provides faster connectivity to the internet. Newer applications are introduced to the market and require fast multimedia-rich data exchange and the number of subscribers soared due to the popularity of smartphones. However, all of that huge data transfer required to travel through the base station or the core network which might create latency.
On the other hand, D2D communication allows devices in close proximity to transfer data by creating a direct link and does not require that data to go through the base station. As a result, latency can be reduced thanks to the shorter traversal path of data.
To enable D2D communication, we can rely on some existing wireless technologies used for transferring data in the near areas such as Bluetooth, WiFi direct, and LTE direct. The listed wireless technologies however offer different ranges and speeds:
- Bluetooth 5.0 offers a maximum data rate of 50Mbps and a range of 240m
- WiFi Direct offers a 250 Mbps data rate and a range of 200m
- LTE Direct offers up to 13.5 Mbps data rate and a range of 500m
In the future, hopefully as the development of location discovery and context-aware services, the cellular network provides may make D2D possible as 4G and 5G can offer higher data rates.
5. Applications of D2D
D2D provides a quick way to send data between devices that are nearby without going through Base Station (BS). That characteristic makes it an effective technique in many scenarios.
Local data services: D2D communication is fit and suitable to provide local data services for a small group of devices. It can support sending from one device to another device (unicast), or group of devices (group cast), or all devices (broadcast).
- Information sharing: by using D2D links we can transfer files, videos, audio with high speed but using lower energy like using cellular channels. When disasters occur, the base stations may be destroyed, however, the D2D links can still work.
- Data and computation offloading: Devices can act as hotspots that contain the same data as BS. Other devices with lower batteries then can get the data of those hotspots.
Machine-to-machine communication: Devices can leverage the power of D2D communication to directly transfer data with lower energy required and ultra-low latency. In some cases, M2M communication requires real-time data to be transmitted. Automation cars need to exchange data with other nearby cars as fast as possible to make a decision instantly.
6. Conclusion
All in all, in this article we have represented some concepts about IoT, M2M, D2D, and some applications of D2D. While IoT refers to a wider system with all types of devices that can ‘talk’ to each other, M2M emphasizes the direct connection between two devices. In addition, D2D communication with its specific features and low cost in both time and energy is a key to enhancing the power of Machine-to-machine.
