In the previous article, we found out about the Internet of Things and 5G Networks. Today, Speranza will give you new concepts that are Industrial IoT and Factory of Things. They are practical applications of the Internet of Things (IoT), which will completely change the face of industry in the world. So, Let’s start.
1. Introduction of Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (abbreviated as IIoT), is a system with a large number of devices, machines, and people connected to each other on an industrial scale such as schools, manufacturing plants,… Sometimes it is also called industry 4.0 or smart manufacturing, there is no clear distinction in these concepts. Industrial devices such as sensors, switches, robots, mechatronics, etc. are interconnected, requiring the acquisition and access of huge data sources at a fast speed to increase accuracy. Therefore, IIoT uses today’s most modern technologies such as cloud computing, machine-to-machine, edge computing, cybersecurity, .. on the basis of the cyber-physical system (CPS) of IoT.
Application of Industrial Internet of Things(IIoT) Source: https://www.rfpage.com/applications-of-industrial-internet-of-things/
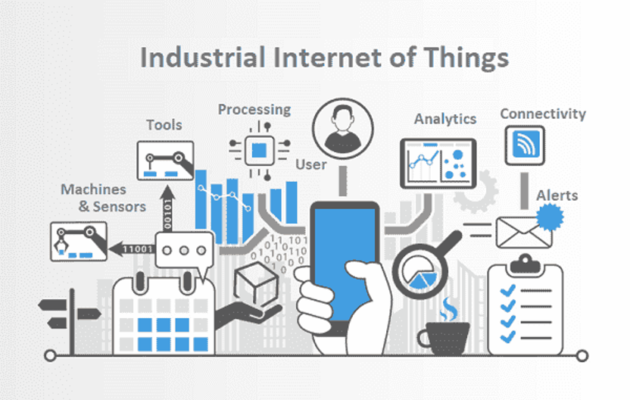
The architecture of the IIoT system is generally not too complicated. It is divided into 4 layers, with data being manipulated in each layer, and transferred from the bottom to the top. Those layers are:
– Device layer: the bottom layer, referring to the physical devices in the system such as robots, sensors,…
– Network layer: is the data transport layer in IIoT. This layer includes cloud computing, network protocols via buses.
– Service layer: has software to control equipment, process data, and display it on the control panel.
– Content layer: is the graphics interface of the device in the system, for example, smart surfaces, screens, tablets, PoS stations, etc.
2. Industrial Internet of Things – Next level factory
In the scope of this article, we can consider the Industrial Internet of Things equivalent to the Smart Factory, although the Factory of Things as defined in the scientific report of Professor Detlef Zuehlke in a higher degree. These are fairly new concepts, available in very developed countries because of the high level of proficiency required.
Smart Factory describes a factory using mechanisms of automation and optimization, where machinery and equipment improved most effective processes. It is built on today’s most advanced technologies such as AI (artificial intelligence), Big data, IIoT along advanced business management systems like ERP or MES… When everything is “Internet chemistry”, operators can control access to the equipment in their factory at any time, just have phones connected to the Internet.

Smart factory without worker to operate Source: https://www.avnet.com/wps/portal/abacus/resources/article/the-origins-of-industry-4-0/
What makes Smart Factory’s strength is its ability to grow and adapt throughout operations. Whether it can be changed by market demand, opening new markets, or developing other products, the production process is still changed in real-time. In addition, AI-integrated sensors can predict and respond to operational and maintenance needs, incorporating new technologies and processes.
3. From traditional industry to modern industry by IIoT.
Changing a tradition is not easy, especially when it has been going on for hundreds of years. Today’s manufacturing industry is the product of the industrial revolution in Britain hundreds of years ago. There is too much labor in the factory, and the operating costs are enormous. Imagine a process that requires 10 workers to operate, must have a responsible manager, when replacing with machines, only 1 operator is needed!

Traditional factories need many workers. Source: https://www.sfexaminer.com/news-columnists/broken-fashion-industry-needs-mending/
IIoT helps to transform the traditional way of production from man-work to machine-operated and man-managed. In addition, accuracy is enhanced when the devices are pre-programmed. Because all connected, the system can understand the entire production process and make decisions on its own. Processes will have “autonomy” in a hierarchical module system.

Outstanding benefits when IIoT was applied Source: https://www.plantautomation-technology.com/articles/benefits-of-implementing-industry-40-in-the-manufacturing-industry
The Industrial Internet of Things can completely change the technological status of industrial factories in the future. . According to Shoplogix statistics, in 2018 more than 1.67 billion dollars poured into IIoT platforms for the manufacturing industry. It is predicted that by 2024 that number will be more than $12.44 billion, achieving a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of nearly 40% for 7 consecutive years, a huge number. The largest global market for the IIoT platform is manufacturing, the estimated value is $438 million by 2021[[1]].
4. Challenges when applying IIoT
Besides the great effects, challenges are also inevitable if Smart Factory is deployed. The first is the linkage, devices and machines use different protocols leading to difficulties in operation. And each device and machine is connected to the Internet, so there is a high risk of being attacked by hackers. Different sensors and networking infrastructure can lead to multiple vulnerabilities. Companies need to ensure the absolute security of their data. Currently, there is a fairly secure protocol called MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport). In the future, there will certainly be many improvements to bring optimal efficiency when IIoT was applies more widely.
Conclusion
With the information provided above, hope you have an understanding of Industrial IoT and Factory of Things. In the digital era, transforming to new technologies is inevitable. IIoT and Factory of Things are expected to bring optimal efficiency to the manufacturing industry around the world.
As a pioneer in IoT Industry, Speranza has more than 5 years of experience to develop enterprise-level IoT applications. Speranza provides a comprehensive solution for your business, with 2 services IoT Consulting & IoT App Development.
Reference Source
- Wikipedia. (2021). Industrial Internet of Things. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Industrial_internet_of_things
- Detlef Zuehlke. (2010). SmartFactory – Towards a factory-of-things. Available at: http://foresight.ifmo.ru/ict/shared/files/201311/1_124.pdf
- Thales Group. (2021). Smart manufacturing and the IoT are driving the Industry 4.0 revolution. Available at: https://www.thalesgroup.com/en/markets/digital-identity-and-security/iot/inspired/smart-manufacturing
